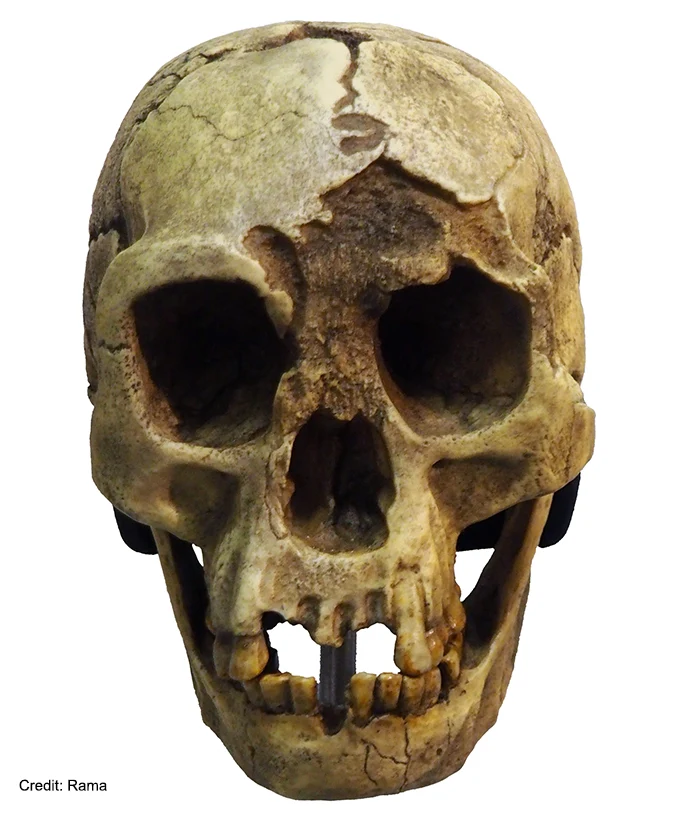
BLOG - On October 28, 2004, a paper was published in Nature describing the dwarf hominin we know today as Homo floresiensis that has shocked the world. The report changed the geographical landscape of early humans that previously stated that the Pleistocene Asia was only represented by two species, Homo erectus and Homo sapiens.
The report titled "A new small-bodied hominin from the Late Pleistocene of Flores, Indonesia" written by Peter Brown and Mike J. Morwood from the University of New England with Thomas Sutikna, Raden Pandji Soejono, Jatmiko, E. Wahyu Saptomo and Rokus Awe Due from the National Archaeology Research Institute (ARKENAS), Indonesia, presents more diversity in the genus Homo.
“Immediately, my fever vanished. I couldn’t sleep well that night. I couldn’t wait for sunrise. In the early morning we went to the site, and when we arrived in the cave, I didn’t say a thing because both my mind and heart couldn’t handle this incredible moment. I just went down to the pit and looked at the bones carefully. It would be impossible to get them out because of the condition of the bones. So we decided to cut the remains out, together with the sediment, block by block, and bring them back to the hotel. We needed several days to take out all the bones,” said Sutikna, tells his story of the discovery..
Their findings sparked a decades-long debate over the evolutionary origins of the "Hobbits of Flores" whose skeletons were excavated at the Liang Bua site and inhabited a small island in Indonesia. Did H. floresiensis descend from ancient hominins more than 700,000 years ago? Were they simply a dwarism of Asian Homo erectus or Homo habilis and Australopithecus afarensis from Africa?
Sutikna has loved cultural history since junior high school and wanted to become a cultural figure. He felt he could learn about the history of human life, culture and environment, from prehistoric times to the present.
"When I graduated from high school, I only registered at Sebelas Maret University (UNS) in Surakarta, but I had to take two tests. In 1983, the entrance test was screened twice, as far as I remember it only happened in 1983 and coincidentally until the second test," he recalled.
Sutikna's desire to study history and culture in more depth grew stronger when he started taking courses in Ancient Indonesian History at the History Department, Faculty of Literature, UNS. In 1990, he went to Jakarta and got to know Prof. Dr. Raden Pandji Soejono, an Indonesian archaeology figure and began to be involved in research activities at several archaeological sites in Indonesia
"Since 1993 I started studying archaeology with Prof. Soejono and became his assistant. Since then I began to study archaeology autodidactically. Two years is not enough to study archaeology autodidactically, because it turns out it is not as easy as what we see in the famous Indiana Jones films," he recalled.
In 1995, after having a daughter, he took a Masters in Archaeology at the Faculty of Cultural Sciences at the University of Indonesia and his involvement in archaeological research became wider. Sutikno began to be actively involved in interdisciplinary archaeological research, including geology, geochronology, paleontology and paleoanthropology.
Soejono and Morwood led excavations at the Liang Bua site from 2001 to 2004 in a collaborative project between ARKENAS and the University of New England. This research was conducted together with Sutikna, Saptomo, Jatmiko and Rokus Awe Due.
Sutikna and his colleagues successfully discovered H. floresiensis on September 2, 2003 after finding parts of a stegodon when Benyamin Tarus's sledgehammer scratched the eyebrow of the ancient human skull. They managed to find nine skulls with one intact skull named "LB1" as the holotype.
At that time, Sutikna and his colleagues estimated that LB1 was around 18,000-38,000 years old, but in further research they revised it to a minimum of 50,000 years. Sutikna and other teams in a recent study reported that H. floresiensis bones from excavations at the Mata Menge site were 700,000 years old.
"The discovery of the ancient human Homo floresiensis in Flores, also known as the 'Hobbit' in 2003, was the biggest discovery during my time studying archaeology. This discovery has a huge impact on our understanding of the early history of human life," said Sutikna.
Flores was previously never considered in the migration route of ancient humans because it was separated by the ocean, in addition for more than a decade, the discovery of the ancient human from Flores has been a hot debate. Since the first discovery, Sutikna has been involved in research projects with many researchers and has been the author of more than 27 papers related to the ancient human skeleton from Flores.
Read more:
Brown, P., Sutikna, T., Morwood, M. et al. A new small-bodied hominin from the Late Pleistocene of Flores, Indonesia. Nature 431, 1055–1061 (2004). DOI:10.1038/nature02999.
Callaway, E. The discovery of Homo floresiensis: Tales of the hobbit. Nature 514, 422–426 (2014). DOI:10.1038/514422a.
Drs. Thomas Sutikna, M.Hum. Salah Satu Ilmuwan Paling Berpengaruh di Dunia. Sebelas Maret University, Maret 23, 2015.
The ancestor of Homo floresiensis lived 700,000 years ago was smaller, Dlium, August 6, 2024.
By Aryo Bandoro
Founder of Dlium.com. You can follow him on X: @Abandoro.
The report titled "A new small-bodied hominin from the Late Pleistocene of Flores, Indonesia" written by Peter Brown and Mike J. Morwood from the University of New England with Thomas Sutikna, Raden Pandji Soejono, Jatmiko, E. Wahyu Saptomo and Rokus Awe Due from the National Archaeology Research Institute (ARKENAS), Indonesia, presents more diversity in the genus Homo.
“Immediately, my fever vanished. I couldn’t sleep well that night. I couldn’t wait for sunrise. In the early morning we went to the site, and when we arrived in the cave, I didn’t say a thing because both my mind and heart couldn’t handle this incredible moment. I just went down to the pit and looked at the bones carefully. It would be impossible to get them out because of the condition of the bones. So we decided to cut the remains out, together with the sediment, block by block, and bring them back to the hotel. We needed several days to take out all the bones,” said Sutikna, tells his story of the discovery..
Their findings sparked a decades-long debate over the evolutionary origins of the "Hobbits of Flores" whose skeletons were excavated at the Liang Bua site and inhabited a small island in Indonesia. Did H. floresiensis descend from ancient hominins more than 700,000 years ago? Were they simply a dwarism of Asian Homo erectus or Homo habilis and Australopithecus afarensis from Africa?
Sutikna has loved cultural history since junior high school and wanted to become a cultural figure. He felt he could learn about the history of human life, culture and environment, from prehistoric times to the present.
"When I graduated from high school, I only registered at Sebelas Maret University (UNS) in Surakarta, but I had to take two tests. In 1983, the entrance test was screened twice, as far as I remember it only happened in 1983 and coincidentally until the second test," he recalled.
Sutikna's desire to study history and culture in more depth grew stronger when he started taking courses in Ancient Indonesian History at the History Department, Faculty of Literature, UNS. In 1990, he went to Jakarta and got to know Prof. Dr. Raden Pandji Soejono, an Indonesian archaeology figure and began to be involved in research activities at several archaeological sites in Indonesia
"Since 1993 I started studying archaeology with Prof. Soejono and became his assistant. Since then I began to study archaeology autodidactically. Two years is not enough to study archaeology autodidactically, because it turns out it is not as easy as what we see in the famous Indiana Jones films," he recalled.
In 1995, after having a daughter, he took a Masters in Archaeology at the Faculty of Cultural Sciences at the University of Indonesia and his involvement in archaeological research became wider. Sutikno began to be actively involved in interdisciplinary archaeological research, including geology, geochronology, paleontology and paleoanthropology.
Soejono and Morwood led excavations at the Liang Bua site from 2001 to 2004 in a collaborative project between ARKENAS and the University of New England. This research was conducted together with Sutikna, Saptomo, Jatmiko and Rokus Awe Due.
Sutikna and his colleagues successfully discovered H. floresiensis on September 2, 2003 after finding parts of a stegodon when Benyamin Tarus's sledgehammer scratched the eyebrow of the ancient human skull. They managed to find nine skulls with one intact skull named "LB1" as the holotype.
At that time, Sutikna and his colleagues estimated that LB1 was around 18,000-38,000 years old, but in further research they revised it to a minimum of 50,000 years. Sutikna and other teams in a recent study reported that H. floresiensis bones from excavations at the Mata Menge site were 700,000 years old.
"The discovery of the ancient human Homo floresiensis in Flores, also known as the 'Hobbit' in 2003, was the biggest discovery during my time studying archaeology. This discovery has a huge impact on our understanding of the early history of human life," said Sutikna.
Flores was previously never considered in the migration route of ancient humans because it was separated by the ocean, in addition for more than a decade, the discovery of the ancient human from Flores has been a hot debate. Since the first discovery, Sutikna has been involved in research projects with many researchers and has been the author of more than 27 papers related to the ancient human skeleton from Flores.
Read more:
Brown, P., Sutikna, T., Morwood, M. et al. A new small-bodied hominin from the Late Pleistocene of Flores, Indonesia. Nature 431, 1055–1061 (2004). DOI:10.1038/nature02999.
Callaway, E. The discovery of Homo floresiensis: Tales of the hobbit. Nature 514, 422–426 (2014). DOI:10.1038/514422a.
Drs. Thomas Sutikna, M.Hum. Salah Satu Ilmuwan Paling Berpengaruh di Dunia. Sebelas Maret University, Maret 23, 2015.
The ancestor of Homo floresiensis lived 700,000 years ago was smaller, Dlium, August 6, 2024.
By Aryo Bandoro
Founder of Dlium.com. You can follow him on X: @Abandoro.